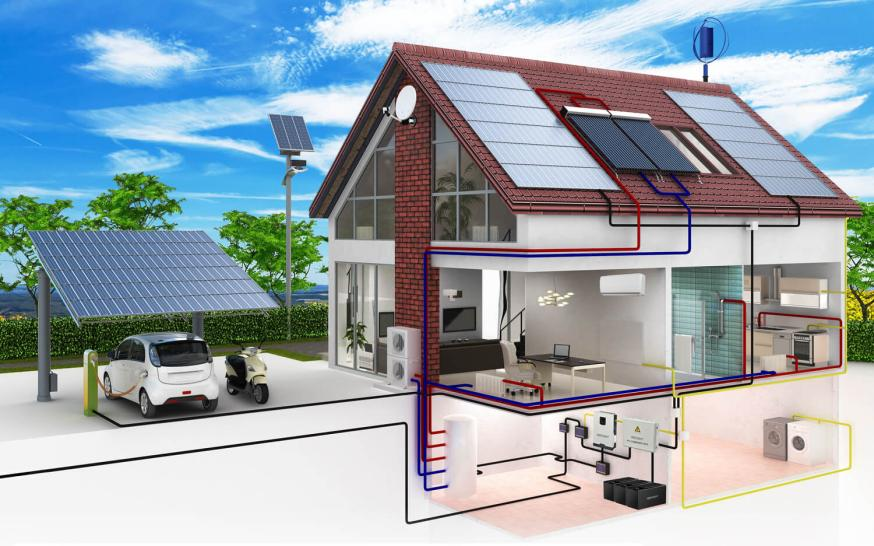
The inverter market has undergone significant transformations in recent years, playing a pivotal role in the energy sector's transition towards cleaner and more efficient technologies. From residential solar installations to industrial power systems, inverters have become an essential component for converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) – a fundamental requirement for powering a wide range of devices. This blog post delves into the evolution of the inverter market, its current landscape, and the exciting prospects that lie ahead.
The development of inverters
The history of inverters dates back to the early 20th century, where they were primarily used in telecommunications and radio equipment. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that inverters started gaining traction in the energy sector due to the increasing popularity of solar power systems. Early inverters were large, inefficient, and expensive, limiting their widespread adoption.
Technological Advancements
As technology progressed, so did the capabilities of inverters. The shift towards more advanced semiconductor materials and improved power electronics paved the way for smaller, more efficient, and cost-effective inverters. This evolution has been particularly evident in the solar industry, where string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers have become the norm, allowing for enhanced energy production, system monitoring, and overall reliability.
Market Trends and Drivers
Several factors have contributed to the growth of the inverter market:
- Renewable Energy Integration: The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, has driven the demand for inverters to efficiently convert the generated DC into usable AC power for homes, businesses, and the grid.
- Grid Modernization: As power grids become smarter and more interconnected, inverters play a crucial role in enabling grid stability through functionalities like voltage regulation, frequency control, and reactive power compensation.
- Energy Storage: The rise of energy storage systems, such as batteries, has further amplified the demand for inverters. These devices enable the efficient charging and discharging of batteries, making it possible to store excess energy for use during peak demand periods.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Inverters are integral components in electric vehicle charging infrastructure, converting AC power from charging stations to DC power for battery charging.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the remarkable progress in the inverter market, challenges remain:
- Efficiency Enhancement: While inverters have become significantly more efficient, there is ongoing research to further improve their conversion efficiency, reducing energy losses and increasing overall system performance.
- Grid Integration: As more distributed energy resources come online, inverters must be equipped to seamlessly integrate with diverse grid environments, helping to maintain grid stability and reliability.
- Cost Reduction: Cost remains a factor, especially for larger-scale installations. Continued advancements in manufacturing processes and materials can help drive down costs and make renewable energy systems more economically viable.
The Future of the Inverter Market
Looking ahead, the inverter market is poised for exciting developments:
- Advanced Grid Support: Inverters will play a more active role in grid support, participating in grid-balancing activities and offering enhanced functionalities to ensure stable and reliable power supply.
- Hybrid Systems: The integration of multiple energy sources, such as solar, wind, and energy storage, will lead to the emergence of hybrid systems that rely on sophisticated inverters to manage the diverse energy flows.
- Digitalization and Smart Features: Inverters will incorporate advanced monitoring, control, and communication capabilities, allowing users to optimize energy usage, track performance, and remotely manage their systems.
- Emerging Markets: As renewable energy adoption grows in emerging markets, the demand for reliable and efficient inverters will surge, offering opportunities for market expansion.